Looking To The Future – What Is 5G?
It doesn’t seem that long ago when the first 4G smartphone hit the market, yet the wireless industry is already preparing for 5G. As each of the four worldwide mobile phone carriers are getting ready to bring us 5G, smart phone chipmakers, and major network equipment companies are joining the race to provide their customers with the “ultra-fast” 5G network.
However there are numerous hurdles which the industry will have to jump over before we will be seeing the 5G symbol on our smartphones any time soon. The reasoning for this? It has yet to be decided what 5G even means, let alone what it will look like when it finally arrives. What we do know is that 5G will soon become a necessity.
So what is 5G?
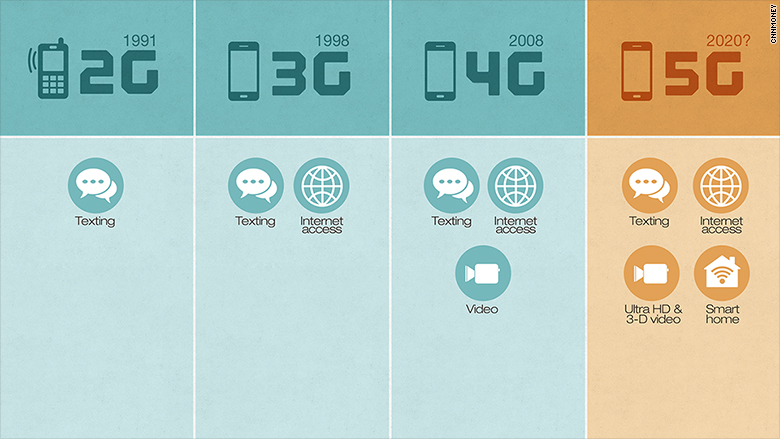
The “G” in 3G, 4G, and 5G simply stands for “generation”, so 5G will be the fifth generation of the wireless network technology. But there seems to be one slight problem, the standards for 5G have not yet been disclosed and we probably won’t find out for another few years.
According to Bill Smith, the president of AT&T’s network operations, 5G will likely be defined by 2018, and the standards will hopefully be codified sometime in 2019 by the International Telecommunications Union branch of the United Nations. These standards will determine which wireless networks can be classified at 5G, and what characteristics it must include.
The current predictions for 5G is that it will be faster, smarter, and less power-hungry than the current 4G, enabling a slew of new wireless gadgets. 5G will also allow us to have faster smartphones, more smart-home devices and longer-lasting wearable technology.
Another alleged characteristic of 5G is the ultra-low latency, meaning that it could drastically reduce the period of time it takes for the network to respond to your command.
How fast is fast?
Rumor has is that 5G has the potential to offer speeds up to 40x faster than your current 4G network – fast enough to stream a 3D 8K video in about 6 seconds versus the current 6 minutes. However, we need to remember that there is a difference between lab experiments and reality. As we get excited about downloading the latest 3D movie to our smartphone in 6 seconds, we might forget that in the real world, speeds are much slower than promised.
Nokia, who is currently leading the way for 5G development believes that their 5G technology will allow for real-time speeds of about 100 Megabits per second when the connection is most congested – this is already 4x faster than our current 4G’s top speed.
But what about interference? Just like your Sirius XM radio you may find your network dropping out when going under bridges and concrete, driving on the freeway, and through densely populated tree areas. Why? Numerous wireless companies are experimenting with 5G on super high frequency networks, up to as high as 73,000 MHz. Our current mobile networks are broadcasting signals in a range of 700 – 3,500 MHz’s, so this increase is as massive. This means that the signals will be travelling at shorter distances and may struggle to penetrate walls, resulting in the need to have thousands of mini mobile towers on every lamppost and in every room.
But what will 5G bring?
As technology is advancing we need a stronger ultra-fast network to keep up and meet our demands. 5G has the potential to fill the in the gaps that our preventing us from getting to the next stage of technology design and production.
For the sports fans out there, 5G could allow for video multi-tasking. This could create the ability to equip sports stadiums with cameras to enable viewers to recieve a live feed of the game to their smartphone or tablet. Not just this, you could potentially switch the camera angles and rewind for real-life playbacks all in stunning 4K.
For the general public, 5G is said to increase the safety of self-driving cars, which is a big plus after the current Google car crash a few months back. With most self-driving cars being powered by wireless networks, having a network to reduce the lag time between the car sensors and the data sending center will be a highly valued improvement all around.
And finally the gaming industry has the potential to revolutionise with 5G completely changing your virtual reality world. Nokia believes that with 5G, virtual reality users will be able to collaborate as if they were in the same physical location, creating a new era of video gaming.
So when will 5G arrive?
There has not been an overall consensus as to when 5G will be ready for mass deployment, however several counties are planning on testing the new network at the 2018 Winter Olympics and the 2019 Summer Olympics. But here in the US, Verizon is allegedly working on bringing 5G to market as soon as 2017.
How will it preform? No one turely knows yet, but it is clear that 5G will be changing the way we connect with world around us.
